How to loosen a bowel blockage at home
What to know about bowel obstruction and blockage
A bowel obstruction is a blockage in the small or the large intestine. It can happen for many reasons, and can lead to severe complications. Dietary measures can help manage symptoms while waiting for treatment or a resolution.
In this article, we examine the symptoms and causes of bowel obstruction. We also look at how doctors can treat this condition and what people can do to prevent it from occurring.
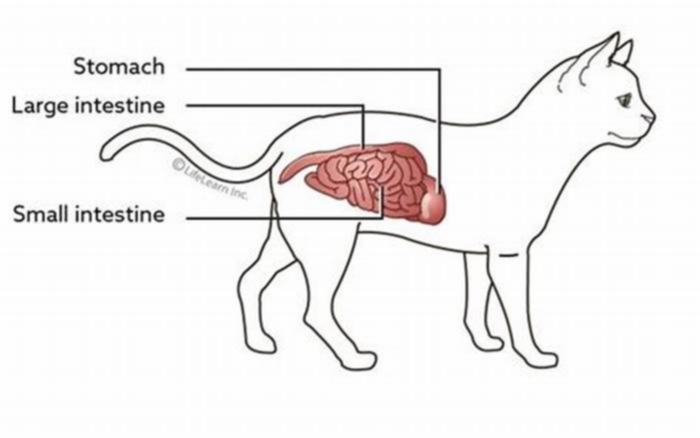
The term bowel obstruction refers to blockages in the intestines that are not the result of fecal matter.
- twisting of the intestines
- a hernia
- inflammation
- tumors
- adhesions, or scar tissue, from surgery
Obstructions result in a buildup of food, gastric acids, gas, and fluids. As these continue to accumulate, pressure in the bowel increases. This can result in a rupture or split. Whatever was behind the blockage can enter the abdominal cavity and spread bacteria.
Bowel obstructions can vary in severity. Some only partially obstruct the intestines, while others cause complete blockages.
Most bowel obstructions require treatment. Medication and bowel rest may treat mild cases, while surgery is necessary in around
Types of bowel obstructions
Bowel obstructions can vary depending on the severity of the blockage:
- Complete obstructions: Severe bowel obstruction can entirely block part of the intestine. This may stop all solids, liquids, and gases from passing through the digestive system. Someone with a complete obstruction will find passing a stool or gas difficult, if not impossible.
- Partial obstructions: A partial bowel obstruction is typically less severe. These obstructions block some, but not all, of the intestine. This will slow the progress of solids, liquids, and gases through the digestive system but will not stop them entirely. A partial bowel obstruction may cause discomfort, bloating, and diarrhea.
- Pseudo-obstruction: Intestinal pseudo-obstruction is a
rare condition that causes the symptoms of bowel obstruction without the presence of a blockage. It occurs when muscle or nerve issues prevent the normal movement of food, liquids, and gas through the intestines.
Bowel obstructions can be painful and distressing. Symptoms include:
Vomiting and diarrhea are
If a fever develops after some of these symptoms, it can be a sign of an infection, and a person should consult a doctor.
There are many possible causes of bowel obstruction. They are either mechanical or nonmechanical.
Mechanical obstructions
Mechanical obstructions are physical barriers that prevent or restrict the flow of matter through the bowels. These include:
Nonmechanical obstructions
The large and small bowels move in coordinated contractions. If something interrupts this process, a nonmechanical obstruction can occur.
If a doctor can detect and treat the cause, bowel obstruction is usually a short-term issue.
Some people refer to
Causes of nonmechanical bowel obstructions include:
Some conditions and events increase the risk of a bowel obstruction occurring, such as:
Bowel obstructions and age
People of any age may experience full or partial bowel obstructions. However, obstructions can carry additional complications in younger children and older adults.
Bowel obstructions are a
Small bowel obstructions are also a
If severe abdominal pain develops, a person should contact a doctor immediately.
Bowel obstruction can have serious consequences. An individual should seek medical advice if they experience any symptoms of a bowel obstruction.
Diagnosis tends to begin with a physical examination. An obstruction can cause a hard lump in the abdomen, which a doctor may be able to feel. The doctor will also assess a persons medical history during the initial examination.
A doctor can use a stethoscope to check a persons bowel activity. A lack of regular bowel sounds or unusually quiet sounds can suggest a bowel obstruction.
Depending on individual cases, a doctor may recommend further tests. These can include:
- blood tests to check levels of electrolytes, liver and kidney function, and blood counts
- endoscopy, in which a doctor uses a special camera to look inside the gut
- CT scans
- X-rays
- contrast enemas
Treatment for bowel obstruction depends on the cause and how severe the blockage is.
A total mechanical obstruction usually requires surgery. Most cases of bowel obstruction need some form of medical intervention.
Treatment options for bowel obstruction can include:
- Medication: Opioids can lead to constipation. If this occurs, laxatives and stool softeners can help.
- Observation: Doctors will typically observe a person with partial or complete obstructions before considering further options, such as surgery. During this time, the individual should limit their food and drink intake to stop further buildup. Doctors can provide fluid intravenously, meaning directly into the vein, to keep the person hydrated.
- Nasogastric tube: This is a narrow tube that goes up the nose and into the stomach. It removes fluid and gas trapped in the stomach, relieving pressure. This eases pain and vomiting.
- Surgery: Surgeons can remove blocked or damaged sections of the bowel. In cases of IBDs, a strictureplasty may be necessary. Here, a surgeon will widen the narrowed section of the bowel by cutting and sewing.
- Therapeutic enema: A nurse or doctor will push a medication or tap water into the bowel to try to relieve stool impaction, which can happen in severe constipation.
Medication may help ease discomfort due to a bowel obstruction. This can include:
- antinausea medicines to prevent vomiting
- pain relief medication
- antibiotics to fight bacterial infection
People should try to move around when possible and remain hydrated to ensure their electrolytes are balanced.
Those with Crohns disease may benefit from steroids.
A bowel obstruction can lead to other issues, such as:
People who have had surgery for obstructions are also at risk of other complications, including:
At worst, it can lead to multiple organ failure and death. That is why it is important to treat bowel obstructions as soon as possible.
Simple changes to a persons diet and lifestyle can help them digest food more easily and lower the impact of bowel obstructions.
To help prevent bowel obstruction, a person can aim to:
- drink plenty of water to remain hydrated
- exercise regularly
- chew their foods well
- eat smaller meals throughout the day
If a person is at risk of bowel obstruction, a doctor may recommend avoiding foods that are high in dietary fiber. Reducing the fiber content in a persons diet aims to reduce the amount of stool and reduce how often a person may need to empty their bowels.
The following table outlines some foods to eat:
A bowel obstruction occurs when something blocks part of the small or the large intestine. It is vital to take this condition seriously and seek immediate medical attention.
Tumors, scar tissue from surgery, and abnormalities in a persons intestinal development can all cause bowel obstructions.
Bowel obstructions can lead to severe complications. In extreme cases, they can cause intestinal ruptures and be deadly if a person does not receive timely treatment.
Individuals can lower their risk of developing an obstruction by eating well, keeping active, and staying hydrated.
The outlook for a bowel obstruction depends on its cause. In most cases, bowel obstruction is treatable.
Read the article in Spanish.
How do you treat a fecal impaction?
Fecal impaction is when a hard, dry mass of stool becomes stuck in the colon or rectum. If laxatives and suppositories do not help, enema, water irrigation, or manual evacuation may be necessary.
Prompt medical help for constipation can avoid fecal impaction, which can lead to damage in the rectum and other complications. If fecal impaction occurs, there are several treatment options.
Here, find out about the options for treating a fecal impaction.
A doctor may recommend oral laxatives,
A person should take the tablet as the doctor, pharmacist, or instruction leaflet advises.
Polyethylene glycol comes as a powder to dissolve in water or another drink. A person may need to take it for 24 days to produce a bowel movement. It makes the colon produce more water, which softens the mass, allowing the body to pass it through and excrete it.
A person should take bisacodyl tablets with water and can expect a bowel movement in 612 hours with bisacodyl. It is a stimulant which triggers the rectum to move the feces forward.
Laxatives are available over the counter, but it is best to check with a doctor before using them. They may not be safe to use with certain conditions, such as a bowel obstruction.
What is the difference between a stool softener and a laxative?
People can buy glycerin and bisacodyl suppositories over the counter, without a prescription. A person will need to insert the suppository into the rectum and wait for it to act.
Glycerin
Bisacodyl triggers defecation by acting on neurons in the rectum. A bowel movement should occur within 1560 minutes. These suppositories are not suitable for children under 6 years of age.
Always follow the directions on the packet or a doctor or pharmacists instructions.
If laxatives and suppositories do not help, a person can use an enema. In an emergency, a doctor may do this.
In an enema, a person will insert a fluid into the rectum that softens the stool and makes it easier to push out. The fluid may be a saline solution or a solution of water and one of the following ingredients, depending on where the impaction is:
The process of applying an enema is as follows:
- The person will insert a tube into the anus.
- They will administer small amounts of enema to help reduce discomfort.
- The person should try to hold in the fluid for 15 minutes to allow the feces to dissolve.
- The individual may then massage the lower abdomen gently to encourage the fluid and feces to leave the body.
- A person may need to have several enemas until the liquid leaving the body is clear.
- An enema may be uncomfortable but should not be painful. If there is pain, the person should tell the doctor.
After removing impacted stool, a person may need to take additional laxatives or fiber supplements and to drink extra water to prevent a recurrence.
There are many types of enema, but people should check with a doctor before using any type.
During water irrigation a doctor will insert a small hose into the rectum and flush the area with water, encouraging the stool to soften and break down.
A doctor may massage the rectum after this procedure to help the stool move through, before removing it via another tube.
If an enema fails to work, it may be necessary to break the stool down and remove it by hand. Removing the stool should result in a persons bowel movements returning to normal, and any side effects should go away.
A doctor
- apply lubrication
- use the index finger to gently break up and remove the impacted feces
- use equipment such as an anoscope to see inside the rectum and suction, if necessary
In severe cases, a doctor may need to carry out this process in a surgical setting.
People with a fecal impaction should not try to remove the mass by themselves or wait for it to go away.
Instead, they should seek medical advice. A doctor will advise them on the best approach.
After treatment for fecal impaction, a person
Not seeking prompt treatment for fecal impaction can lead to:
People should seek help if they have a change in bowel movements lasting longer than 2 weeks or if they use any type of laxative for more than 1 week without constipation resolving.
Anyone who suspects they have a problem with their colon or digestive health should speak with a doctor as soon as possible.
A diet that promotes healthy bowel movements will be high in fiber.
It may
Other strategies that can help prevent or manage constipation include:
- taking regular exercise
- avoiding processed foods
- doing bowel training to establish regular bowel habits
- speaking with a doctor about the possible side effects of any new medications
Fecal impaction can result from severe or untreated constipation. Not treating it can lead to severe complications.
Prompt treatment will minimize discomfort and the risk of complications and may lead to the diagnosis of an underlying condition that needs treatment.
Diet and lifestyle changes can help prevent constipation and avoid a reoccurrence.